2nd Generation STING Agonist
A signaling molecule that plays a critical role in the cytosolic detection of tumor-derived DNA
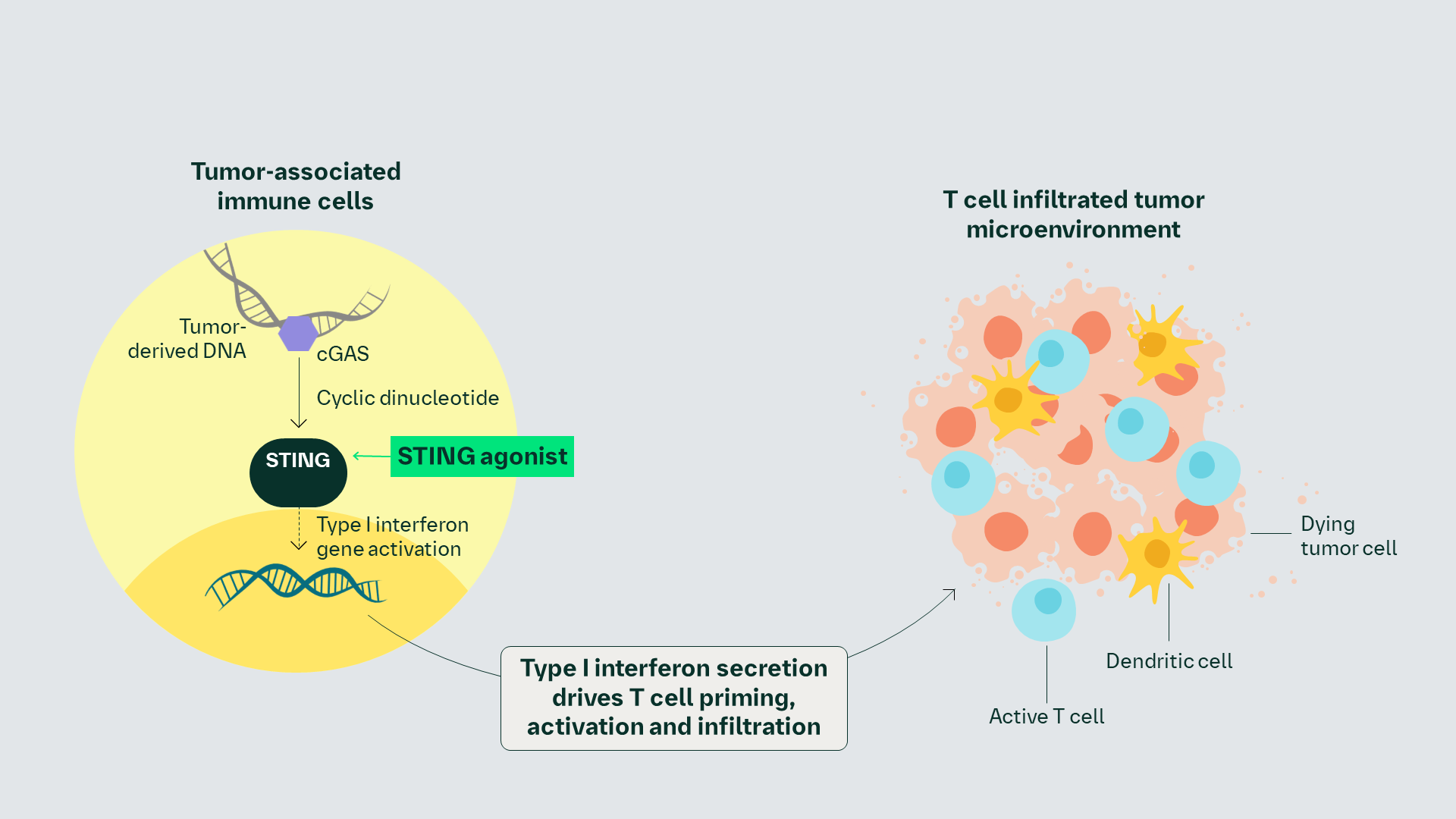
2nd Generation STING Agonist Proposed MoA
| Status | Phase 1 |
|---|---|
| Patient population | Solid Tumors |
| Combination partners | PD-1 inhibitor-ezabenlimab |
Molecule
BI 1703880 is a systemic small-molecule agonist of STING.1 STING functions as a DNA sensor and is expressed in immune cells, stromal cells and tumor cells.1,2
Proposed MoA
STING pathway activation by 2nd generation STING agonist induces the production of type I IFN and inflammatory cytokine secretion in the TME, leading to innate immune cell activation, cross-priming, activation, and infiltration of cytotoxic T cells and subsequent tumor cell killing.1–3
Preclinical data have shown that BI 1703880 potently and highly selectively activates the STING pathway, resulting in dose-dependent cytokine secretion.
Combination therapy
In vivo data (preclinical mouse tumor models) demonstrated induction of a tumor-specific immune response leading to complete antitumor response when administered in combination with anti–PD-1.4
BI 1703880 is currently being investigated in a Phase I trial in combination with ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) in patients with advanced solid tumors.5
Proposed MoA1
1. Harrington K, et al. SITC 2022. Abstract 626; 2. Woo SR. Immunity. 2014;41:830–842; 3. Barber GN. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015;15:760–770; 4. Gremel G, et al. Cancer Res. 2020;80(16 Suppl): Abstract 4522; 5. NCT05471856. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05471856. Accessed April 2024.
Clinical Research and Development
2nd Generation STING Agonist Clinical Trial
| Trial number | Phase | Compound | Patient population | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | BI 1703880 + ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) | Advanced solid tumors | Recruiting |
BI 1703880 is a small molecule that is intended to bind to the stimulator of interferon genes (STING) 1,2
BI 1703880 may selectively activate the STING pathway, resulting in dose-dependent local tumor control and the induction of a tumor-specific immune response1
The 2nd generation STING agonist in combination with ezabenlimab is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial for the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors3
1. Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file; 2. Woo SR. Immunity. 2014;41(5):830–42; 3. NCT05471856. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05471856. Accessed October 2023.
Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file.
Woo SR. Immunity. 2014;41(5):830–42.
NCT05471856. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05471856. Accessed October 2023.
Doi T, et al. JSMO 2022. Poster 370268.
You may also be interested in...

OUR PIPELINE