B7-H6/CD3 T-cell Engager
A first-in-class IgG-like T-cell engager targeting B7-H61
B7-H6/CD3 T-cell Engager Proposed MoA
| Status | Phase 1 |
|---|---|
| Patient population | CRC and solid tumors expressing B7-H6 |
| Combination partners | ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) |
Molecule
B7-H6 is a member of the B7 family of immune receptors, which is expressed in several solid tumor indications, such as CRC, NSCLC, HNSCC, hepatocellular, gastric, and pancreatic carcinoma while no to very little expression can be detected in normal tissues.1,2
The B7-H6/CD3 T-cell engager is a first-in-class IgG-like T-cell engager targeting B7-H6.1
Proposed MoA
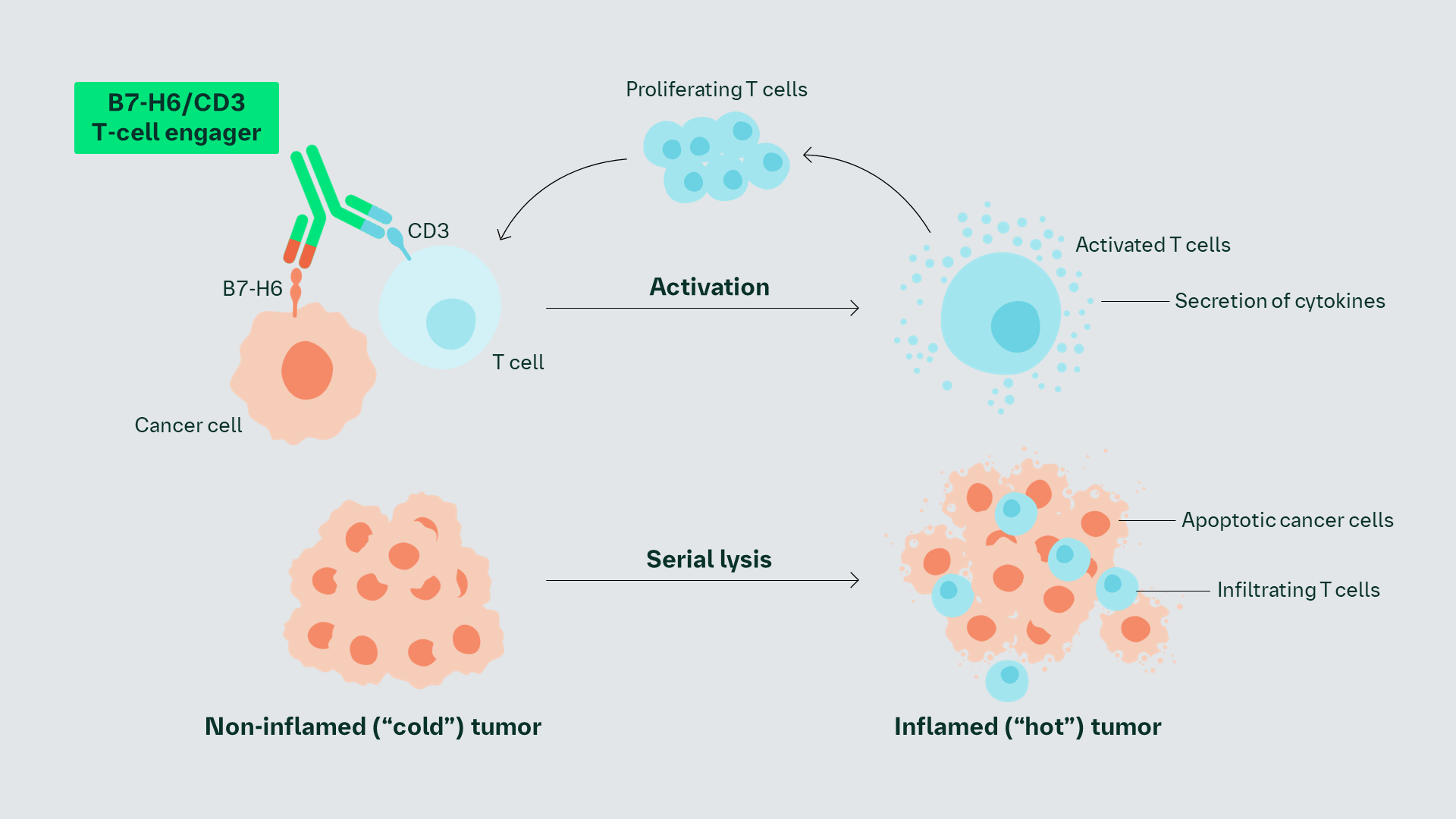
The pharmacologic effect of the B7-H6/CD3 T-cell engager depends on its simultaneous binding to both the CD3 subunit of the T-cell receptor complex as well as to B7-H6 on tumor cells; targeted for elimination. This results in lysis of B7-H6-positive target cells, activation and proliferation of T cells, and secretion of cytokines.1
B7-H6/CD3 T-cell engager does not block interaction of B7-H6 with its natural ligand Nkp30, allowing B7-H6–dependent NK-cell activation and cytotoxicity.1
Proposed MoA1,2
Preclinical data and combination therapy rationale
B7-H6/CD3 monotherapy induced tumor regression in in vivo models and infiltration of T cells into tumor tissues (converting ‘cold’ tumors into ‘hot’ tumors).1
Based on the upregulation of PD-1 in these models, combination with anti-PD1 may further enhance the efficacy.1
Clinical Research and Development
B7-H6/CD3 T-cell Engager Clinical Trial
| Trial number | Phase | Compound | Patient population | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1 | BI 765049 ± ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) | Advanced, unresectable, and/or metastatic solid tumors expressing B7-H6 (i.e. CRC, NSCLC, HCC, HNSCC, gastric carcinoma and pancreatic carcinoma) | Recruiting | |
NCT06091930 (1454.4) | 1 | BI 765049 ± ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) | Malignant solid tumors expressing B7-H6 | Recruiting |
B7-H6/CD3 is a novel IgG-like T-cell engager which may simultaneously bind to the CD3 subunit of the T-cell receptor complex and to B7-H6 on tumor cells targeted for elimination, without interfering with B7-H6–dependent NK-cell activation and cytotoxicity1,2
Preclinical data demonstrated the B7-H6/CD3 T-cell engager to be highly B7-H6–selective and efficacious in inducing T-cell activation, tumor tissue infiltration, and tumor cell death, resulting in conversion of a non-inflamed into an inflamed tumor environment2
BI 765049 ± ezabenlimab is currently being evaluated in an ongoing Phase 1 study in patients with advanced B7-H6–expressing solid tumors3
1. Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file; 2. Hipp S, et al. AACR 2021. Oral Presentation 56; 3. NCT04752215. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT04752215. Accessed October 2023; 4. Falchook GS et al. ASCO 2022. Poster TPS3175.
Hipp S, et al. AACR 2021. Oral Presentation 56.
Brandt C, et al. J Exp Med. 2009;206(7):1495–1503.
NCT04752215. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/study/NCT04752215. Accessed October 2023.
Falchook GS, et al. ASCO 2022. Poster TPS3175.
Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file.
You may also be interested in...

OUR PIPELINE
DLL3/CD3 T-CELL ENGAGER