CD137 FAP Agonist
CD137 FAP Agonist-BI 765179
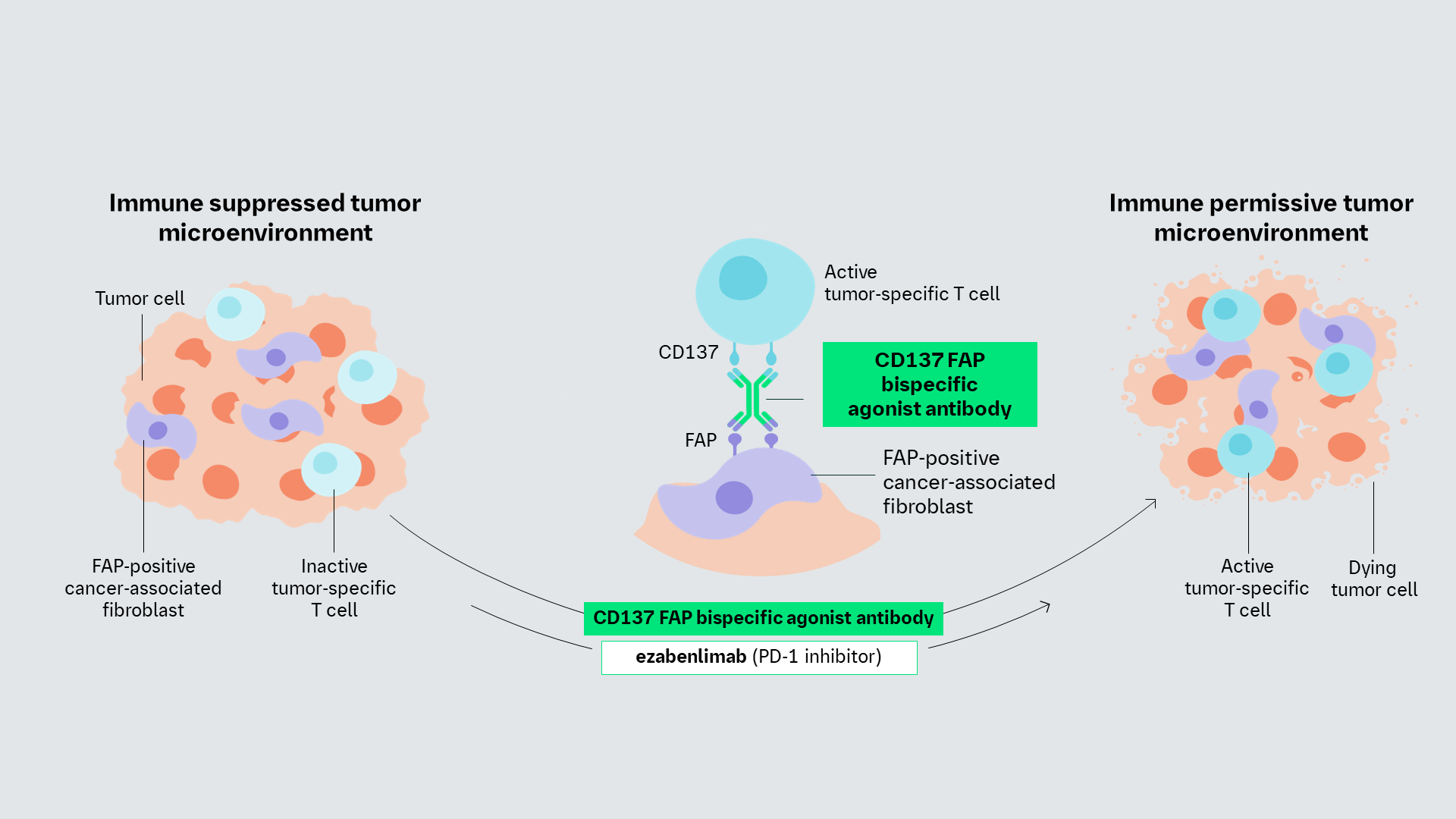
Our CD137 FAP bispecific antibody* is designed to act as a CD137 agonist only upon simultaneous binding to CD137 and FAP leading to tumor-restricted activation of tumor-specific CD137+ T-cells.
CD137/FAP Bispecific Agonist Antibody Proposed MoA
| Status | Phase 1 |
|---|---|
| Patient population | Solid tumors |
| Combination partners | PD-1 inhibitor-ezabenlimab |
Molecule
The CD137/FAP bispecific antibody is designed to act as a CD137 agonist only upon simultaneous binding to CD137 and FAP leading to tumor-restricted activation of tumor-specific CD137+ T-cells.
Proposed MoA
CD137 is a receptor expressed on immune cells including T cells, NK cells, and dendritic cells, that functions as an important regulator of immune responses and is an essential pathway for maximal CD4 and CD8 T cell responses. Fibroblast activation protein (FAP) is a protein expressed on cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs).
CD137/FAP antibody may selectively reactivate T cells within the TME in a tissue-dependent manner via concomitant binding to FAP on CAFs, and CD137 on T cells, avoiding systemic activation of T cells and associated cytotoxicity.
Combination therapy rationale
Combination with anti-PD-1 can boost tumor-specific T cell activity further by both releasing tumor-mediated suppression of T cells and simultaneously activating the T cells through CD137 agonism.
Proposed MoA
Clinical Research and Development
CD137/FAP Bispecific Agonist Antibody Clinical Trial
| Trial number | Phase | Compound | Patient population | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|
1a | BI 765179 (CD137/FAP bispecific agonist antibody) ± ezabenlimab (PD-1 inhibitor) | Advanced solid tumors | Recruiting |
CD137/FAP agonist is a bispecific antibody that may bind concomitantly to FAP on CAFs and CD137 on T cells within the TME, leading to a FAP-dependent activation of tumor-infiltrating T cells and subsequent lysis of tumor cells1
The CD137/FAP bispecific agonist antibody is currently being evaluated in a Phase 1 clinical trial for the treatment of patients with advanced solid tumors2
1. Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file; 2. NCT04958239. https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT04958239. Accessed October 2023.
- Boehringer Ingelheim. Data on file.

OUR PIPELINE